how to stop laptop from booting
Learn various methods to safely stop your laptop from booting, whether for troubleshooting, maintenance, or other technical purposes.
There are several reasons why you might need to stop your laptop from booting, such as troubleshooting startup issues, performing maintenance, or accessing recovery options. This guide will walk you through various methods to achieve this safely.
Warning: Interrupting the boot process improperly can lead to data loss or system damage. Always ensure you have important data backed up before proceeding.
Method 1: Using the Power Button
This is the most straightforward method:
- Start your laptop as you normally would.
- As soon as you see any sign of booting (e.g., manufacturer logo), press and hold the power button.
- Keep holding until the laptop shuts off completely (usually 5-10 seconds).
Note: This method should be used sparingly as it can potentially lead to data corruption if done frequently.
Method 2: Accessing BIOS/UEFI
Entering BIOS/UEFI will prevent the normal boot process:
- Start or restart your laptop.
- As soon as the first screen appears, repeatedly press the BIOS key. This key varies by manufacturer:
- Dell, HP: F2 or F10
- Lenovo: F1 or F2
- Acer: F2 or Delete
- ASUS: F2 or Delete
- If successful, you’ll enter the BIOS/UEFI setup screen, stopping the normal boot process.
Tip: If you’re unsure of your BIOS key, check your laptop’s manual or look for on-screen prompts during startup.
Method 3: Boot Menu
Accessing the boot menu can interrupt the normal boot sequence:
- Start or restart your laptop.
- Immediately start pressing the boot menu key. Common keys include:
- Esc
- F12
- F9
- If successful, you’ll see a menu of boot options, halting the normal boot process.
Method 4: Recovery Environment (Windows)
For Windows laptops, you can force entry into the recovery environment:
- Turn on your laptop.
- As soon as you see the Windows logo, press and hold the power button to force a shutdown.
- Repeat this process three times.
- On the fourth boot attempt, Windows should automatically enter the recovery environment.
Note: This method is specific to Windows 10 and 11.
Method 5: Remove the Battery (If Applicable)
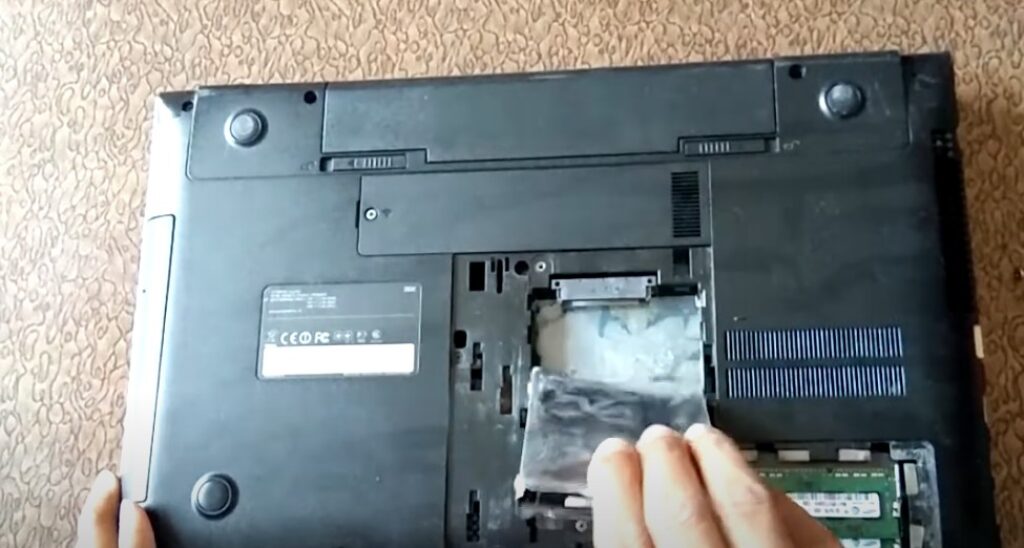

For laptops with removable batteries:
- Shut down your laptop completely.
- Unplug the power adapter.
- Flip the laptop over and locate the battery compartment.
- Remove the battery following your laptop’s specific instructions.
- With the battery removed, the laptop cannot boot.
Caution: This method doesn’t apply to laptops with non-removable batteries. Attempting to remove a non-removable battery can damage your laptop and void your warranty.
When to Stop Your Laptop from Booting
Common scenarios where you might need to stop the boot process include:
- Troubleshooting startup issues
- Accessing recovery options
- Performing hardware maintenance or upgrades
- Attempting to recover data from a non-booting system
Safety Precautions
Before attempting to stop your laptop from booting, consider these safety measures:
- Back up important data regularly
- Use a surge protector to prevent damage from power fluctuations
- If you’re uncomfortable with these procedures, consult a professional technician
- For hardware-related methods, ensure your laptop is unplugged and you’re grounded to prevent static discharge
Risks and Consequences
Before attempting to stop your laptop from booting, be aware of these potential risks:
- Data Loss: Interrupting the boot process can lead to data corruption or loss.
- File System Damage: Sudden shutdowns may damage the file system, requiring repair.
- Hardware Stress: Frequent hard shutdowns can stress hardware components.
- Operating System Issues: In some cases, you may need to reinstall or repair the OS.
Always ensure you have recent backups before attempting these methods. For more information on data protection, visit the US-CERT guide on data backup options.
Legal and Warranty Considerations
Be aware of the following:
- Warranty Voiding: Some methods, especially those involving hardware manipulation, may void your warranty.
- Corporate Policies: If this is a work laptop, consult your IT department before attempting these methods.
- Data Protection Laws: Ensure you’re not violating any data protection laws, especially if the laptop contains sensitive information.
For more on consumer electronics warranties, refer to the FTC’s guide on warranty laws.
What to Do After Stopping the Boot Process
Once you’ve successfully stopped the boot process:
- Assess the Situation: Determine why you needed to stop booting and what you need to do next.
- Safe Mode: If troubleshooting, try booting into Safe Mode next.
- Recovery Options: Use system recovery options if you suspect software issues.
- Hardware Check: If you suspect hardware issues, run diagnostic tools or consult a technician.
- Data Recovery: If you can’t boot normally, consider professional data recovery services.
For Windows users, Microsoft provides a guide on recovery options.
Specific Instructions for Mac Users
For Mac laptops, the process can be slightly different:
- Safe Mode: Immediately after turning on your Mac, press and hold the Shift key until you see the login window.
- Recovery Mode: Restart your Mac and immediately press and hold Command (⌘) + R until you see the Apple logo.
- Verbose Mode: Start your Mac and immediately press and hold Command (⌘) + V until you see white text on a black background.
For more detailed Mac troubleshooting, visit Apple’s official support page.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems after stopping the boot process:
- Laptop Won’t Turn On: Ensure it’s charged, try a different power outlet, or consult a technician.
- Continuous Reboot Loop: Try booting in Safe Mode or use recovery options.
- Strange Noises or Smells: Turn off immediately and consult a professional – this could indicate hardware failure.
- Blue Screen of Death (Windows): Note any error codes and consult Microsoft’s support or a technician.
Conclusion
Stopping your laptop from booting can be necessary in certain situations, but it’s not without risks. Always prioritize data backup and safety. When in doubt, consult with a professional technician. Remember, these methods should be used as a last resort in troubleshooting or for specific maintenance tasks.
This information is provided for educational purposes. Always consult your laptop’s manual or a professional technician for model-specific guidance and to ensure you’re not voiding any warranties or violating any policies.






